Chronosphere Telemetry Pipeline
From the creators of calyptia and fluent bit
Control Log Data Cost and Complexity
Control telemetry from source to destination and reduce log data costs by at least 30%. As log data volumes and sources continue to grow, observability and security teams rely on Chronosphere Telemetry Pipeline to:
- Collect data from anywhere
- Transform, enrich, and reduce logs in flight
- Route data to any destination
Telemetry Pipeline is built on open standards and requires 20x less infrastructure resources than other leading pipelines
Telemetry Pipeline Key Benefits
Control Data Volume and Costs
- Filter out low-value logs, remove unneeded fields, and summarize data upstream
- Route log data to low-cost object storage to reduce retention costs
- Ensure your team collects the right data and enforce chargeback models across your organization
Control Complexity
- Control agent sprawl. Centrally manage log collection and aggregation
- Route data to the right destination without blindspots or unwanted duplication
- Manage fleets of Fluent Bit agents. Configure, update, and monitor Fluent Bit deployments at scale
Pre-Process Data for Faster Insights
- Normalize data formats and schema from different sources. Enable your team to query data in a consistent manner
- Enrich data in flight to speed up troubleshooting and investigations
- Redact sensitive information from your logs before data leaves your environment
Avoid Vendor Lock-In
- Speed up observability and SIEM migration by up to 50%
- Stream data to new platforms without installing and configuring new agents
- Reshape data in flight to match the schema requirements of your new SIEM or observability platform
How Our Telemetry Pipeline Works
Collect Data from Any Source
- Aggregate logs from open source log forwarders, like Fluent Bit, FluentD, and OpenTelemetry
- Collect data from enterprise agents and protocols, like Telegraf and Splunk HEC
- Integrate with SaaS Providers, like Okta, Mandiant, and Vercel.
Support other data sources via HTTP API or TCP
Process Data with 25+ Out-of-the-Box Rules
- Transform, enrich, reduce, and secure data before it leaves your environment
- Create custom parsing and processing rules using AI natural language
- Transform data in different ways based on its source or where you’re shipping it
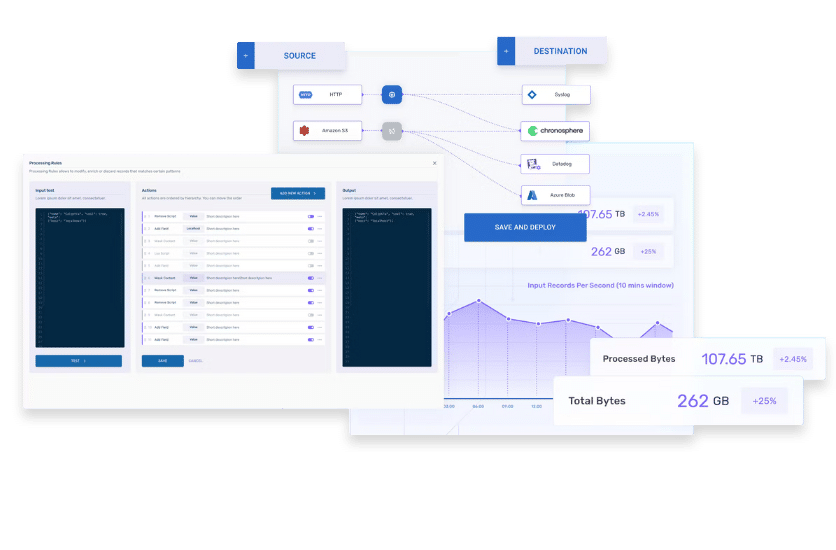
Build Telemetry Pipelines with Flexibility and Ease
- Configure telemetry pipelines using a low code/no code, drag-and-drop builder
- Build, test, and troubleshoot pipelines without interfering with production via the Playground
- Optionally manage telemetry pipelines using a command-line interface (CLI) as needed
Simplify Operations with Kubernetes Native Pipeline
- Built using modern Kubernetes patterns, even when deployed on top of Linux servers
- Scale up particular components of the Telemetry Pipeline without increasing the entire system
- Gain automatic healing, automatic retry, high availability, and load balancing
Enterprise Security and Stability

Chronosphere Telemetry Pipeline is SOC 2 Type II and ISO 27001 examined. Chronosphere guarantees enterprise-level security and stability, supporting various operating systems (including RHEL, Mac, Windows) and providing consistent updates to maintain a secure environment for data operations.
Processing Rules with Chronosphere Telemetry Pipeline Demo
Telemetry Pipeline FAQs
What’s the difference between an observability pipeline and a telemetry pipeline?
“Observability pipeline” and “telemetry pipeline” are interchangeable terms that describe the same technology. Vendors choose different nomenclature based on their preferred terminology.
Chronosphere uses the term “telemetry pipeline” over “observability pipeline" because our offering supports both security and observability use cases.
You might also come across the terms “log pipeline” or “logging pipeline.” That’s because logs are the most common data type processed in a telemetry pipeline. However, Chronosphere Telemetry Pipeline supports all MELT data (metrics, events, log and traces).
How do telemetry pipelines pre-process data?
Telemetry pipelines use stream processing (as opposed to batch processing) to reduce, enrich, transform, and protect log data in flight. Here’s a quick comparison of stream processing and batch processing:
- Batch processing crunches large amounts of data in intervals after it has been grouped together
- Stream processing continuously crunches data as it’s received
Why do observability and security teams use telemetry pipelines to pre-process data?
Observability and security teams use telemetry pipelines for several reasons. Here’s a list of some common use cases for a telemetry pipeline:
- Data redaction helps teams remove sensitive information from their log data. This can include PII masking or the removal of financial information (such as credit card numbers)
- Obfuscation has a similar goal as data redaction – to protect sensitive information. However, obfuscation techniques introduce complexity into the data (versus removing it altogether). Doing so makes it more difficult for third-parties to interpret information
- Data normalization is the process of standardizing logs from different sources. This can include converting all timestamps to a standard format, standardizing IP address formats, or creating a unified taxonomy to classify event types. More ambitious teams might enforce a common schema across all data sources. Data normalization helps observability and security teams locate log data faster by preventing users from querying data sources one-by-one or spending extra cycles trying to craft the “perfect query.”
- Data transformation is an umbrella term that helps support many of the other use cases listed here. It allows you to shape and reduce logs from different sources to meet your observability and security needs. Data transformation includes removing fields, redacting information, structuring logs, and more.
- Data enrichment adds context to your logs from third-party sources. For example, observability teams might enrich logs with information about the cloud region or service owner to enforce chargeback models. Data enrichment can also help security teams investigate threats faster by appending logs with geolocation or threat feed data.
- Data filtering helps teams selectively remove log data based on specific criteria. You might use data filtering to exclude irrelevant records, remove outliers, drop duplicate entries, or retain data that meets certain thresholds. Often, teams might filter out logs below the WARN level and summarize them to reduce their data footprint.
These use cases go beyond basic log aggregation to help teams get data in the right shape for analysis downstream.